Ancient art provides a fascinating window into the cultures, beliefs, and daily lives of early civilizations. Spanning from prehistoric times to the fall of the Roman Empire, ancient art is diverse, reflecting the varied societies that produced it. Here, we explore the key characteristics that define this rich artistic tradition.
Key Characteristics
Here we discuss one by one so connnect with us.
1. Symbolism and Religious Themes
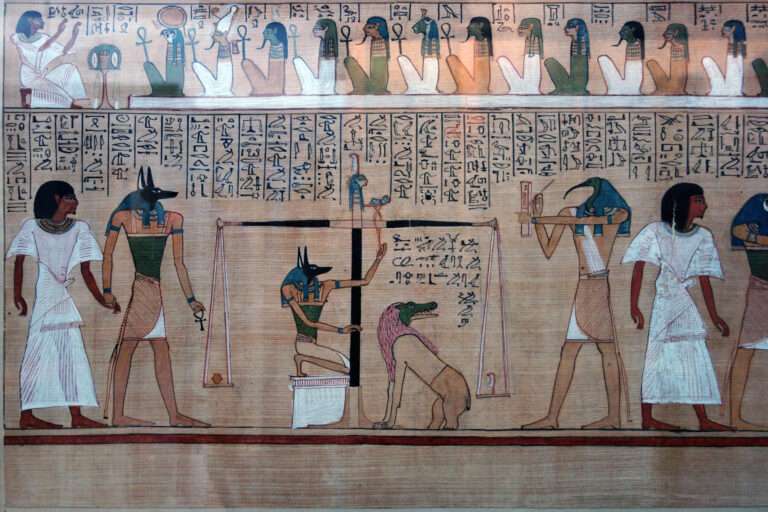
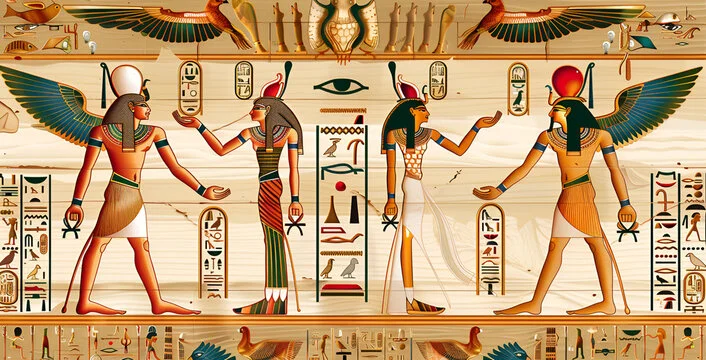
One of the most prominent features of ancient art is its deep connection to religion and symbolism. Many ancient cultures used art to convey spiritual beliefs and honor their gods. For example, in ancient Egypt, artworks often depicted deities, pharaohs, and scenes from the afterlife, emphasizing the importance of the spiritual world. Similarly, Mesopotamian art frequently featured divine beings and mythological creatures, reflecting the region’s complex religious traditions.
2. Functionality
Ancient art was often created with a practical purpose in mind, rather than purely for aesthetic enjoyment. Objects like pottery, tools, and weapons were intricately decorated, blending functionality with artistic expression. For instance, Greek pottery was not only used for storage but also adorned with detailed scenes from mythology and daily life, serving as both a functional item and a storytelling medium.
3. Stylization and Idealization
Ancient artists often stylized their subjects, focusing on idealized forms rather than realistic portrayals. This is evident in Egyptian art, where human figures were depicted with a strict adherence to a standardized, idealized form, with heads and legs shown in profile while torsos were presented frontally. This stylization conveyed a sense of order and divine harmony, which was central to Egyptian culture.
In ancient Greece, the human body was idealized to reflect beauty, strength, and proportion, particularly in sculpture. The Greek concept of arete (excellence) drove artists to create figures that embodied the perfect human form, as seen in the famous statues of athletes and gods.
4. Narrative Art
Ancient art often served as a medium for storytelling, depicting historical events, religious rituals, and mythological tales. This narrative approach can be seen in the elaborate carvings and reliefs of ancient Mesopotamia, which recorded the exploits of kings and gods. Similarly, Roman art frequently celebrated military victories and public events, using detailed friezes and mosaics to tell stories that reinforced the power and achievements of the empire.
5. Use of Natural Materials
Ancient artists primarily used natural materials available in their environment, such as stone, clay, wood, and pigments derived from plants and minerals. The choice of material often dictated the form and durability of the artwork. For instance, the use of durable stone in Egyptian sculpture and architecture contributed to the longevity of these works, many of which have survived for thousands of years.
6. Monumental Scale
Many ancient artworks are notable for their monumental scale, reflecting the power and grandeur of the societies that created them. The Pyramids of Giza, the Colosseum in Rome, and the ziggurats of Mesopotamia are prime examples of how ancient civilizations used art and architecture to express their dominance, religious devotion, and social order.
7. Geometric Patterns and Abstract Designs
Geometric patterns and abstract designs are prevalent in ancient art, particularly in the decorative arts. These patterns were often symbolic, representing cultural beliefs or natural elements. For example, Greek and Roman mosaics commonly featured intricate geometric designs, while Islamic art from the medieval period, which inherited many ancient traditions, is renowned for its complex patterns that avoid figurative imagery in religious contexts.
8. Cultural Identity and Continuity
Ancient art was deeply tied to the cultural identity of a civilization. Artistic styles and motifs were passed down through generations, creating a sense of continuity and preserving the values and traditions of a society. For example, the distinctive art of the Olmecs in Mesoamerica influenced later cultures like the Maya and the Aztecs, illustrating how artistic traditions can persist and evolve over time.
Conclusion
The key characteristics of ancient art—symbolism, functionality, stylization, narrative content, natural materials, monumental scale, geometric patterns, and cultural identity—reveal much about the societies that produced them. These works continue to inspire and inform modern understanding of ancient civilizations, offering a timeless connection to humanity’s past.